Allergy or atopy is inherited genetic condition of the body to react to harmless substances. Allergic rhinitis is an inflammatory disorder of the nasal mucosa induced by allergen exposure
Nose
Nose, the prominent structure between the eyes that serves as the entrance to the respiratory tract and contains the olfactory organ. It provides air for respiration, serves the sense of smell, conditions the air by filtering, warming, and moistening it, and cleans itself of foreign debris extracted from inhalations.
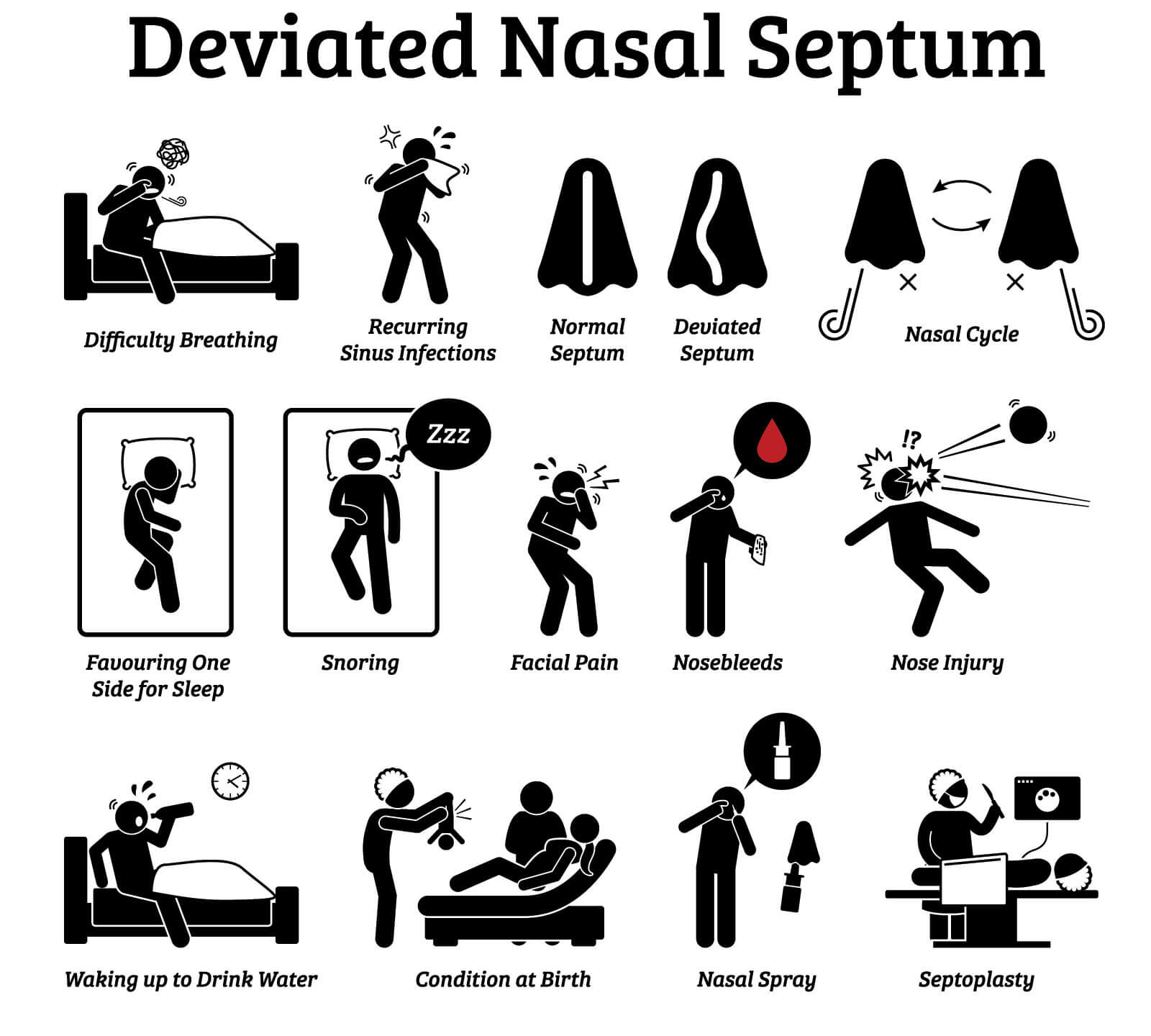
Nose dysfunction can lead to variety of symptoms :
BLOCKED NOSE/ NASAL ALLERGY/ ALLERGIC RHINITIS
it is characterized by four major symptoms–rhinorrhea, sneezing, nasal itching, and nasal congestion. It can also be associated with co-morbid conditions as Asthma, Atopic Dermatitis & Nasal polyps.**
It is based on:
- typical history of allergic symptoms.
- allergic symptoms are those of “sneezers and runners” (Table 1). All patients with persistent allergic rhinitis need a nasal examination (Anterior rhinoscopy, Nasal endoscopy). Functional tests (peak nasal inspiratory flow, rhinomanometry, or acoustic rhinometry) can be used to measure nasal obstruction.
- diagnostic tests.
- In vivo and in vitro tests used to diagnose allergic diseases are directed towards the detection of free or cell-bound IgE. The diagnosis of allergy has been improved by allergen standardization providing satisfactory diagnostic vaccines for most inhalant allergens.
- Immediate hypersensitivity skin tests are widely used to demonstrate an IgE-mediated allergic reaction.
- The measurement of allergen-specific IgE (radioallergosorbent testing, RAST) in serum is of importance and is of similar value to skin tests
- Nasal challenge tests with allergens are commonly used in research. They may be useful, especially in the diagnosis of occupational rhinitis.
A computerized tomography (CT) scan is used to exclude chronic rhinosinusitis, tumors, or when a complication is suspected. - Treatment
The treatment options for your blocked nose depend on the underlying cause and severity of your symptoms; they include medication and surgery. If the cause of your nasal obstruction is rhinitis your specialist may prescribe a course of medication such as an intranasal steroid spray, antihistamines or decongestants. It is important to follow your specialist’s instructions closely.
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Use a nasal decongestant or blow your nose gently to clear your nasal passages.
- Shake the steroidal spray container a few times.
- Close one nostril using index finger.
- Put the nozzle into the open nostril away from the nose’s midline (nasal septum) and spray straight back. Never spray up towards the tip of the nose. This becomes easy if you spray into the right nostril using the left hand and into the left nostril using the right hand.
- Sniff in gently and deeply to activate the spray and exhale through the mouth.
- Now repeat these steps for the other nostril.
Caution: Spray only one nostril at one time. Spray into alternate nostrils each time. Never give two sprays in one nostril. One spray per nostril is sufficient.
RHINORRHEA OR NASAL DISCHARGE
One may define rhinorrhea as a discharge of nasal fluids. It is most commonly a symptom of hay fever and common cold. It may also be symptomatic of drug withdrawal. It is basically caused by the inflammation of the tissues and vessels in the nasal passage. Due to this, it is also referred to as ‘Runny nose’ or ‘Rhinitis’.
- allergic rhinitis
- the ones caused due to some other reason, is referred to as ‘non-allergic rhinitis’.
- Gustatory rhinorrhea is a kind that is caused after eating.
- Another kind is purulent rhinorrhea which is caused due to the side-effects of antibiotics.
- discharge of cerebrospinal fluids, which actually takes place in case of basal skull fracture, it may be referred to as ‘Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea’ or ‘CSF rhinorrhea’.
Allergies, irritation, or any kind of nasal inflammation, yet it may have few more symptoms than a running nose. Besides the discharge of mucosa from the nose which may be clear, yellowish, greenish or even brownish by nature, one may also exhibit other signs. One must be made aware that in case when the nature and colour of the fluid secreted is white, one is said to suffer from clear rhinorrhea.
Some of the other ways by which rhinorrhea may be signalled include nasal congestion caused due to sinusitis, sneezing, headache, dizziness, loss of consciousness or a confused mind, a sore throat, chills, pain in the ear and the face, weariness, bleeding by the nose, breathing problems and even diarrhoea. One may also suffer from cough, erythema and malaise.
However, if running nose is actually underlined by serious traumatic complications, it may exhibit serious symptoms such as fainting, unfettered bleeding, and frequent vomiting. It may actually be triggered by a head injury or an injury to the spine, thereby affecting the nervous system.
ALLERGIES
INFECTIONS
BRONCHIOLITIS
This is also caused by a viral infection and is a significant cause for rhinorrhea in children. Infants are the most common sufferers of the same.
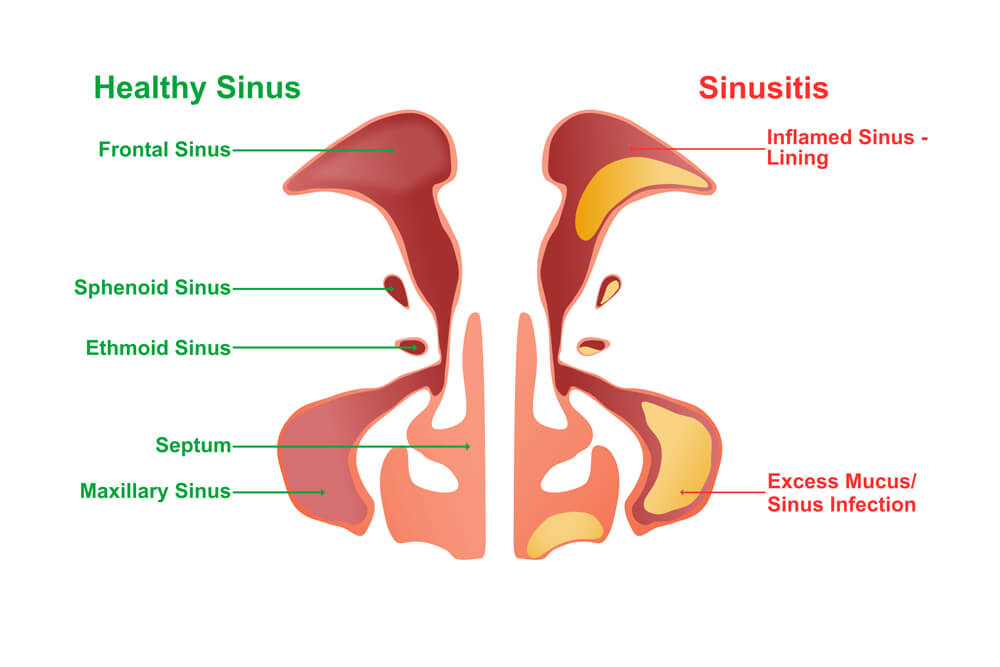
SINUSITIS
IRRITANTS
SPICY FOODS
HEAD INJURY
An injury to the brain and other traumatic experiences may significantly cause rhinorrhea. The nature of this cause may be quite severe. In fact, a basilar skull fracture may be cited as the primary reason for causing cerebrospinal rhinorrhea.
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
Irritants present in the environment such as compounds of disulfide to be found in garlic, shallots and onions, chill and cold air, CS gas or tear gas used as riot control agents, and dry weather are some of the basic reasons behind causing a runny nose. A hypersensitive reaction to such irritants manifests itself in the form of vasomotor rhinitis.
The symptoms of rhinorrhea are a source of indication for the nature and kind of rhinorrhea that one suffers from. The physical examination of rhinorrhea involves an inspection of the face and the nose, especially the area over the maxillary and frontal sinuses. The nature and colour of the nasal mucosa discharged is also taken in for inspection. The rhinorrhea test involves a cell culture of nasal secretions and acid-labile RNA nonenveloped virus test. However, patients suffering from invasive sinusitis, diabetes, and immunocompromised diseases may have to undergo for a CT scan for a proper diagnosis to understand whether one suffers from chronic rhinorrhea or recurrent one.
The treatment of rhinorrhea depends on the underlying cause of the same. Usually it does not require any treatment as it stops by itself but it may have to be dealt seriously in case it is triggered by serious neurological and physical complications.
Medically, rhinorrhea can be treated with the help of.
Topical decongestants such as oxymetazoline and pseudoephedrine also have similar effects. These help in either stopping the discharge or restricting its overflow to a considerable extent.
Along with antihistamines and decongestants, sympathomimetics may also help deal with rhinorrhea. The use of nasal sprays such as vasoconstrictor may also be effective in treating rhinorrhea for a limited period but its overuse may ironically aggravate rhinorrhea and may also lead to rhinitis medicamentosa. Such sprays help in fighting rhinorrhea caused due to allergies. All such medications are available over the counter but it is advisable to take them under the supervision of a doctor. They especially provide for an effective CSF rhinorrhea treatment.
Besides the aforementioned, one may also go for nasal irrigation which involves cleaning and rinsing the nose with saline water. One may be alleviated from the problem by increasing the volume of fluid intake and increase in the humidity in the air. This may be done by drinking lots of fruit juices or water and using a warm or cool mist humidifier. The basic motive in this attempt is to make the mucus thin.
BLEEDING FROM NOSE( EPISTAXIS).
Infection i.e. rhinosinusitis
- Allergic and nonallergic rhinitis
- Use of blood thinning drugs
- Trauma that can also be self-inflicted through actions such as nose picking. This is commoner in children.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Alcohol abuse
- Pregnant women undergoing hormonal changes
- In rare cases, nosebleeds can be due to tumours or inherited bleeding disorders
Actually tackling a common nosebleed is easy and does not require help from a doctor. Of course, you should know the correct first-aid steps which we are outlining below:
- Use your index finger and thumb to pinch together the soft part of the nose.
- Compress the pinched part of the nose towards the face bones.
- Lean forward a bit and tilt the head forward as well. This will stop blood from running back into sinuses and throat which can lead to gagging or inhalation of blood.
- Keep on holding the pinched nose for minimum 5 minutes. Repeat the entire process until nosebleed stops.
- Keep the head higher than the level of the heart. Do not lie down. Do not put your head between your legs. Just sit quietly.
- Wrap some ice in towel and place it on cheeks and nose.
- If the problem recurs, visit your ENT physician for a checkup.
While most nosebleeds are the common type and can be handled at home, you need to watch out for the following symptoms and rush to the hospital immediately:
- If the bleeding is unstoppable or keeps happening again and again.
- If the bleeding is heavy and the blood loss seems considerable.
- If the patient is feeling faint or weak.
- If the nosebleed is happening due to facial trauma, or is accompanied by loss of consciousness or blurred vision.
- If the nosebleed is occurring with fever or headache.
- Last but not the least, if your infant or toddler gets a nosebleed, visit your pediatrician.